Description
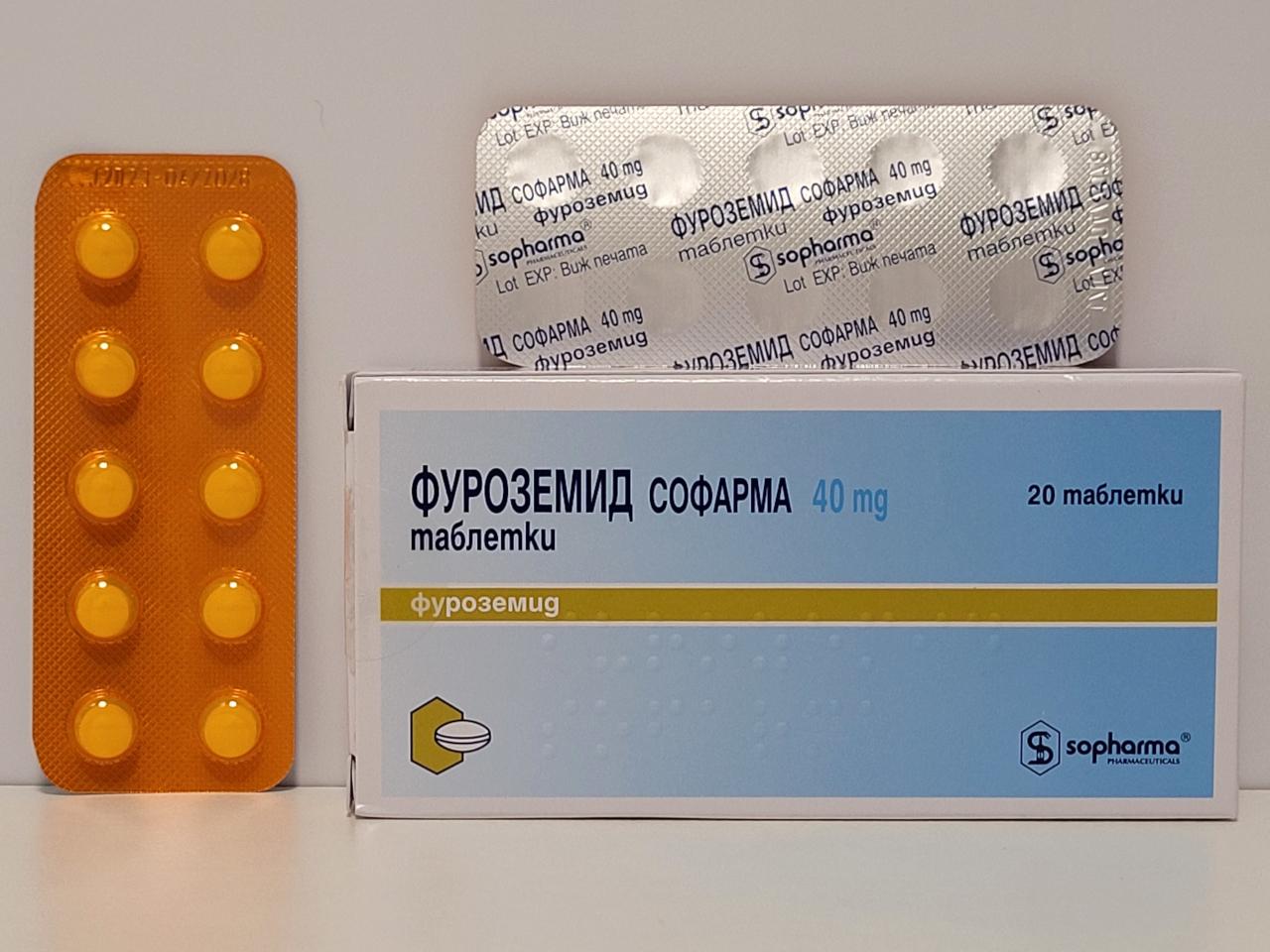
Furosemide belongs to the class of medications called diuretics. It is used to treat edema (fluid retention) that occurs with congestive heart failure and disorders of the liver, kidney, and lung. It is also used to control mild to moderate high blood pressure. It may be used in combination with other medications to treat more severe high blood pressure.
Furosemide works by increasing the amount of urine produced and excreted, and by removing excessive water (edema) from the body. The tablet form begins to work within an hour of being taken and usually lasts for 4 to 6 hours. The injectable form begins to work within 30 minutes and lasts approximately 2 hours.
The recommended adult starting dose for treating edema is 40 mg to 80 mg. If a satisfactory result occurs within 6 hours, the dose may be decreased or kept the same. If edema continues longer than 6 hours, the dose may be increased by 20 mg to 40 mg. The recommended adult daily dose of furosemide ranges from 20 mg to 200 mg. Once the effective single dose has been determined, it may be taken 1 to 3 times a day.
When treating hypertension (high blood pressure), the dose of furosemide starts at 20 mg to 40 mg twice a day. Doses of 40 mg twice a day are generally considered the maximum dose to treat high blood pressure. If blood pressure hasn’t been reduced enough with this dose, other medications may be added to further reduce blood pressure.